Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in men, but it often develops slowly and without obvious symptoms in its early stages. Because early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes, understanding the warning signs and risk factors is crucial.
This article covers the early symptoms of prostate cancer, screening methods, and when to seek medical attention.
Why Early Detection is Important
📌 1 in 8 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime 111.
📌 Early-stage prostate cancer has a 99% survival rate if detected before spreading 222.
📌 Symptoms may be absent or mild at first, so screening is essential.
Who is at Risk?
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing prostate cancer:
✅ Age: Risk increases after 50, and most cases occur in men over 65.
✅ Family History: If a father or brother had prostate cancer, the risk doubles.
✅ Ethnicity: African American men have higher rates and more aggressive forms of prostate cancer.
✅ Genetics: Mutations in BRCA1/BRCA2 genes (linked to breast cancer) can raise risk.
✅ Obesity & Sedentary Lifestyle: Being overweight increases the risk of aggressive prostate cancer 333.
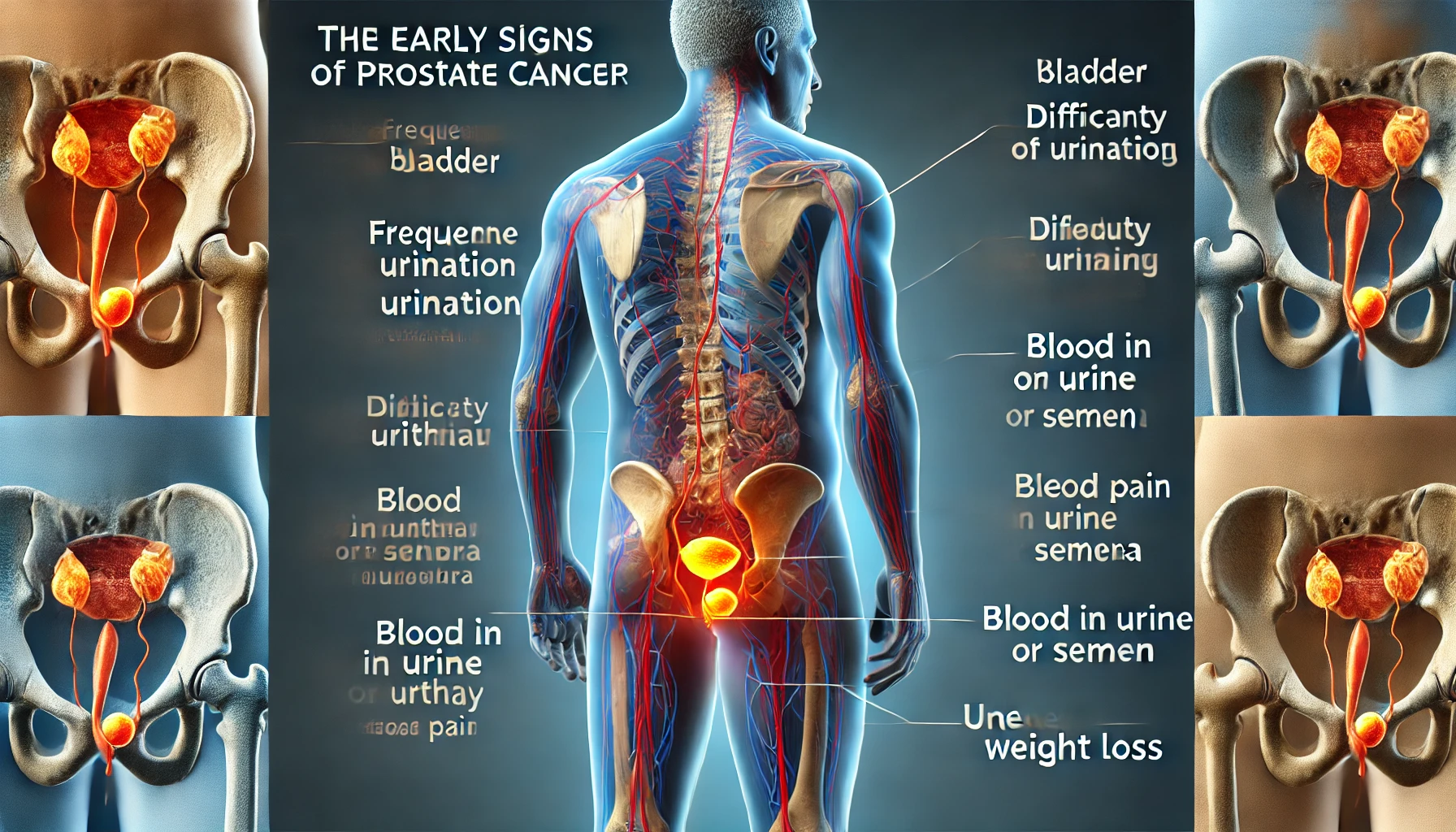
Early Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
📌 Early-stage prostate cancer often has no symptoms. However, as the tumor grows, it may affect urination, ejaculation, and pelvic comfort.
1. Urinary Symptoms
Because the prostate surrounds the urethra, changes in the gland can affect urine flow:
🚨 Warning signs:
🔹 Frequent urination, especially at night (nocturia).
🔹 Difficulty starting or stopping urination.
🔹 Weak or interrupted urine stream.
🔹 Feeling like the bladder doesn’t fully empty.
🔹 Blood in urine (hematuria).
2. Sexual Health Symptoms
Prostate cancer can impact ejaculation and erectile function:
🚨 Warning signs:
🔹 Painful ejaculation.
🔹 Reduced semen volume.
🔹 Erectile dysfunction.
🔹 Blood in semen (hematospermia).
3. Pelvic & Lower Back Pain
If prostate cancer spreads, it may cause persistent pain in the lower back, hips, or pelvis. This can indicate advanced cancer affecting bones.
4. Unexplained Weight Loss & Fatigue
Unintentional weight loss and persistent tiredness may signal advanced prostate cancer, especially if combined with other symptoms.
⚠️ Important: These symptoms can also be caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostatitis. A doctor can determine the cause through proper testing.
How is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed?
Doctors use a combination of screening tests and diagnostic tools:
1. Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test
✔️ Measures PSA levels in the blood.
✔️ Normal levels: Below 4.0 ng/mL, but higher levels may indicate cancer, BPH, or prostatitis.
✔️ PSA levels above 10.0 ng/mL raise strong suspicion of cancer 444.
2. Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
✔️ A doctor manually checks for prostate size, lumps, or irregularities.
✔️ Often used with a PSA test for more accuracy.
3. MRI & Ultrasound Imaging
✔️ Provides detailed images of the prostate to locate suspicious areas.
4. Prostate Biopsy
✔️ A definitive test where tissue samples are examined for cancer cells.
✔️ If cancer is found, a Gleason score determines aggressiveness.
When to See a Doctor
🔹 Men over 50 (or over 40 with risk factors) should have regular PSA and DRE screenings.
🔹 If you experience urinary issues, pain, or blood in urine/semen, see a doctor immediately.
🔹 Regular check-ups help detect prostate cancer early, improving survival chances.
How to Reduce the Risk of Prostate Cancer
✅ Eat a prostate-friendly diet – Lycopene (tomatoes), cruciferous vegetables, and omega-3s help reduce risk.
✅ Exercise regularly – Physical activity lowers cancer risk.
✅ Maintain a healthy weight – Obesity is linked to aggressive cancer.
✅ Limit alcohol & quit smoking – Both increase cancer risk.
✅ Get screened regularly – Early detection saves lives.
Scientific References
- American Cancer Society – Prostate Cancer Statistics (www.cancer.org)
- National Cancer Institute – Early Detection and Survival Rates (www.cancer.gov)
- Harvard Medical School – Obesity and Prostate Cancer Risk (www.health.harvard.edu)
- Mayo Clinic – PSA Test Guidelines (www.mayoclinic.org)
Final Thoughts
Prostate cancer is highly treatable when detected early. Because symptoms may not appear in the early stages, regular screenings are essential.
If you notice urinary changes, blood in urine/semen, or pelvic pain, consult a doctor immediately. Staying proactive can make a life-saving difference.